By Bassem Youssef & Bader Youssef
In 2019, AI, driverless cars, and IoT took centerstage as the promising new technologies that will change the world as we know it. However, the mention of blockchain technology is in passing. Discussions about blockchain usually center around the volatility of Bitcoin’s price, and blockchain’s huge potential reduces to talking about using cryptocurrencies to pay for coffee, pizza, and groceries.
Driverless, electric, and other “smart” cars have been another prominent headline in 2019. Currently, each vehicle can contain an average of 60-100 sensors on board. Because cars are rapidly getting “smarter”, the number of sensors is projected to reach as many as 200 sensors per car. These numbers translate to approximately 22 billion sensors used in the automotive industry per year by 2020.
Regardless of the type of device - whether it be video, audio, or other sensors, IoT-enabled devices all have one thing in common: data. The amount of data that IoT devices send out is borderline ridiculous - so much, in fact, that it is typically measured in zettabytes globally. To put that amount into perspective, one zettabyte is around a billion terabytes of data.
Blockchain can be used for much more than just payments - it can greatly aid in curbing this growing amount of data, as it has the capabilities for IoT devices to securely store, audit, and learn from this massive amount of data on a distributed, fault-tolerant platform.
Using Axon, our blockchain-enabled edge computing device, AI, and the Catapult blockchain, this problem can be overcome to provide a sustainable future for the massive amounts of data to come from IoT.
Gather and Process Data Intelligently With Axon Edge Computing
Simply storing streams of raw data from IoT devices will simply not be enough with the amount of devices to come online - not to mention the bandwidth issues that may arise.
Edge computing is the notion that devices perform computation at the “edge” of the network or at the source of data. It is a distributed computing paradigm that is meant to save on bandwidth and provide a more efficient architecture for devices over a large area. In short - edge computing helps filter relevant data.

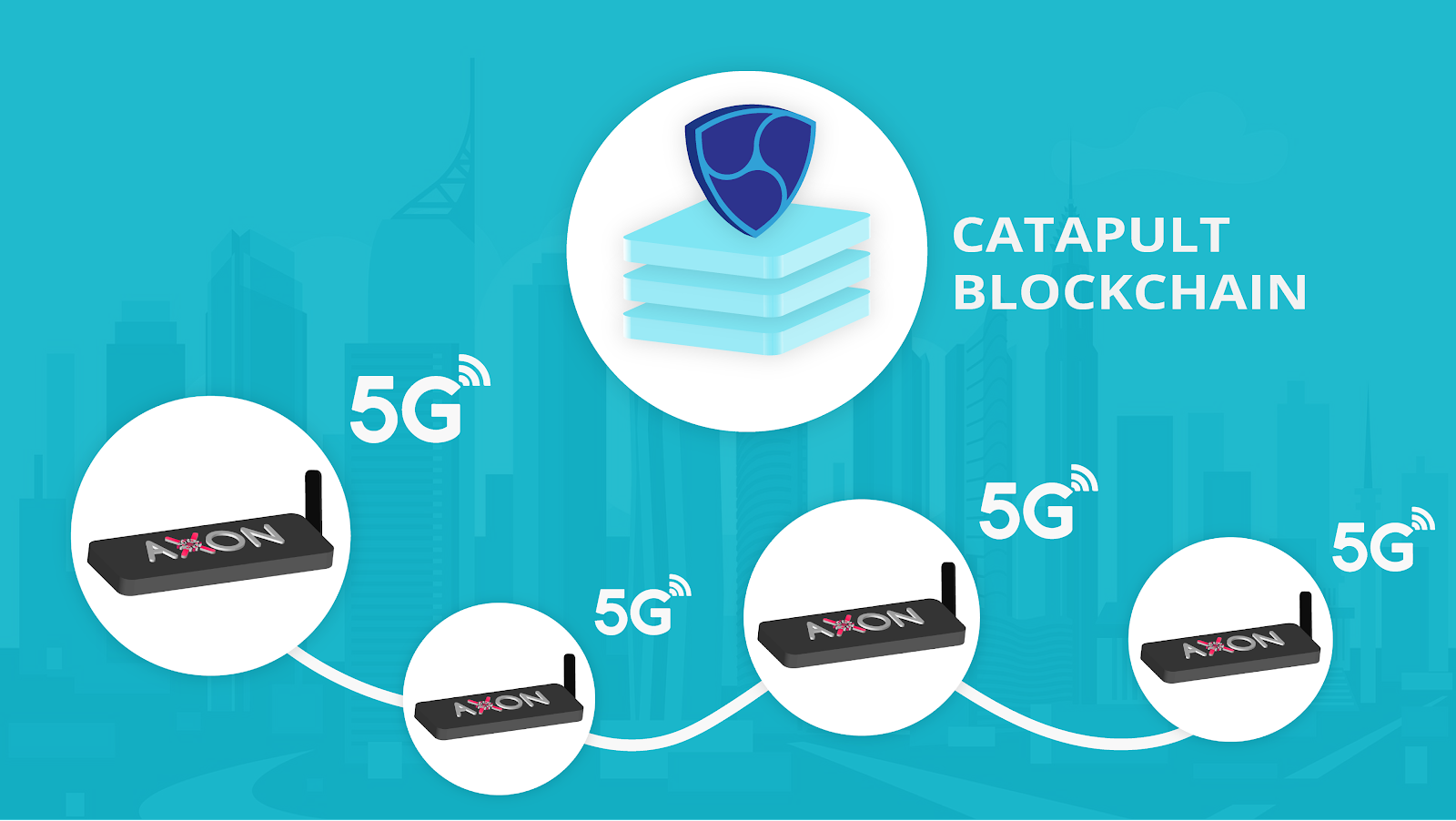
Axon is a multipurpose, blockchain-enabled edge computing device that utilizes this paradigm. Instead of sending raw data to the blockchain, Axon intelligently gathers meaning from the raw sensor data. It is able to integrate with existing technologies to bring blockchain to any level of business due to its efficient and scalable nature.
A perfect example of Axon’s edge computing is the previously mentioned autonomous car. These cars contain sensors that monitor all aspects of the car’s functionality. Each car can generate raw sensor data in the terabytes per day. Most of these autonomous vehicles contain computers powerful enough to perform calculations on the data that it gathers. With edge computing, instead of sending the raw data about the wheel sensor, for example, the car can now calculate the likelihood of the wheel needing replacement on its own.
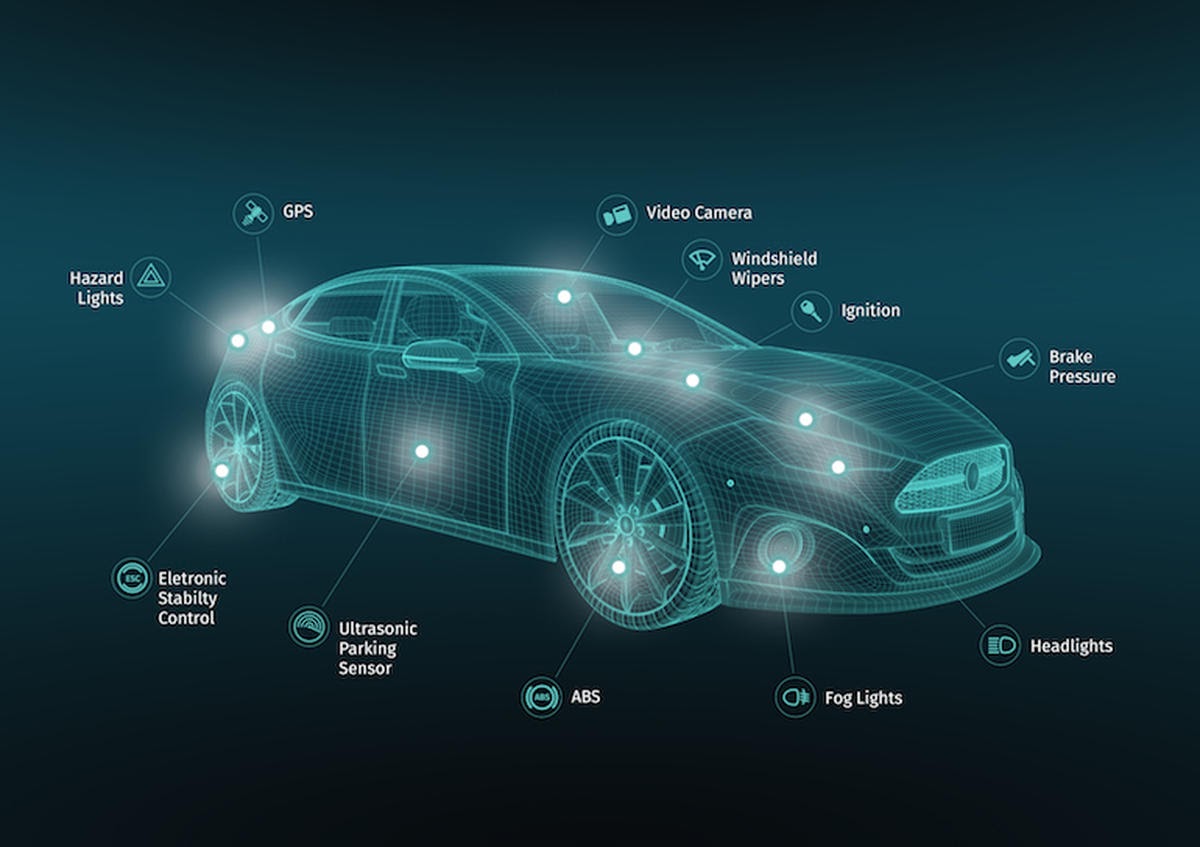
This distributed architecture also provides a more fault tolerant approach to IoT, as devices do not have to rely on a central server for data processing. They are able to be more self-reliant in processing their data.
Big data still has a place, and should never be thrown away. However, using edge computing, we can make IoT more efficient and intelligent by delegating computations for raw data to the device itself.
The advent of 5G has made edge computing even more compelling, enabling significantly improved network capacity, lower latency, higher speeds and increased efficiency. 5G promises data speeds in excess of 20 Gbps and the ability to connect over a million devices per square kilometre.
Garner Meaning From Data Using AI & Swarm Learning

Edge computing allows IoT devices to gather meaningful data at the source, rather than sending it to a central, data processing server. AI is the ability for a machine to learn from the data being fed to it. It allows the user to specify a (usually very large) number of parameters, and adjust those parameters until it is able to make a solid prediction using the given data. AI models can also adjust to new data, and subsequently adjust their model depending on this data.
AI and IoT often are touted as a good combination, as AI can help IoT devices perform a multitude of tasks when it comes to edge computing. An example would be learning when a particular type of aircraft sensor is known to fail, or to provide personalized advice for a hospital patient who interacted with an IoT device within a clinic.
However, just one, low-spec IoT device isn’t going to have enough power to properly compute conclusions from the data using AI. Swarm learning is the concept that multiple devices, or a “swarm”, are able to communicate and share data amongst one another. Essentially, a “swarm” of devices that are recording the same kind of data are able to collectively form an accurate, predictive model based on each other’s inputs.

An example of where swarm learning will be particularly useful is in drone deliveries. Drones in the air can warn other drones of the consequences of flying in certain conditions - together, they are able to learn from one another for different scenarios which some drones in another city may not have encountered before.
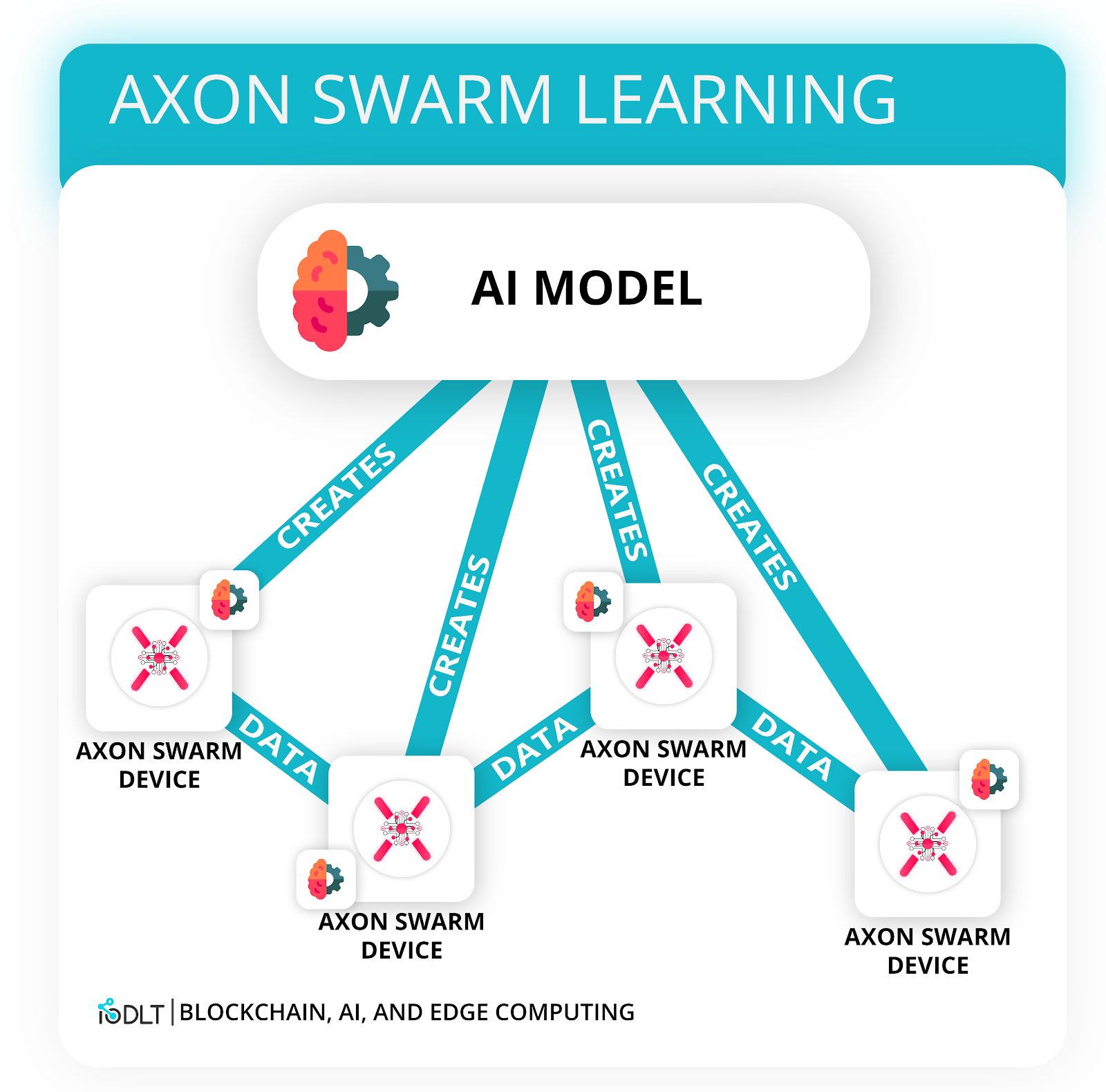
In this context, edge computing devices like Axon are able to communicate with other Axon edge computing devices on a shared, secure network to share their own computations on data. These computations from individual edge devices can then be combined to form a collective predictive model based off of thousands of sensors in the field without the use of the central processing server.
Use Blockchain to Streamline, Share AI models, and Sell Data

The final piece of the puzzle is blockchain: It is quite literally the “glue” that enables all of these technologies to work seamlessly together. Specifically, we will use the NEM Catapult blockchain, as it provides the most practical interface for IoT. Using its REST API interface, IoT devices like Axon can easily utilize Catapult’s functionality to share data from the edge.
Blockchain, like edge computing, is distributed - it syncs the same ledger amongst all of its nodes to provide a redundant and fault tolerant method for recording information.
Edge devices, like Axon, can record their partial AI learnings directly to the blockchain. From here, other edge devices can view data that is sorted on-chain, and further learn from it. The swarm essentially lives on the blockchain, using it as a shared platform of data. After a specified interval of time where the devices are learning from one another, a full conclusion on the edge data can be calculated and stored on-chain. Blockchain enables data to move much more efficiently - as long as only relevant data is recorded to the chain as needed. This helps prevent the zettabytes of data per year that is recorded by IoT devices, and provide a more sustainable future.
Catapult In Action
Catapult exposes many ways sending new information to the blockchain via transactions. Using Catapult’s built-in transaction types, this can quickly become a reality.
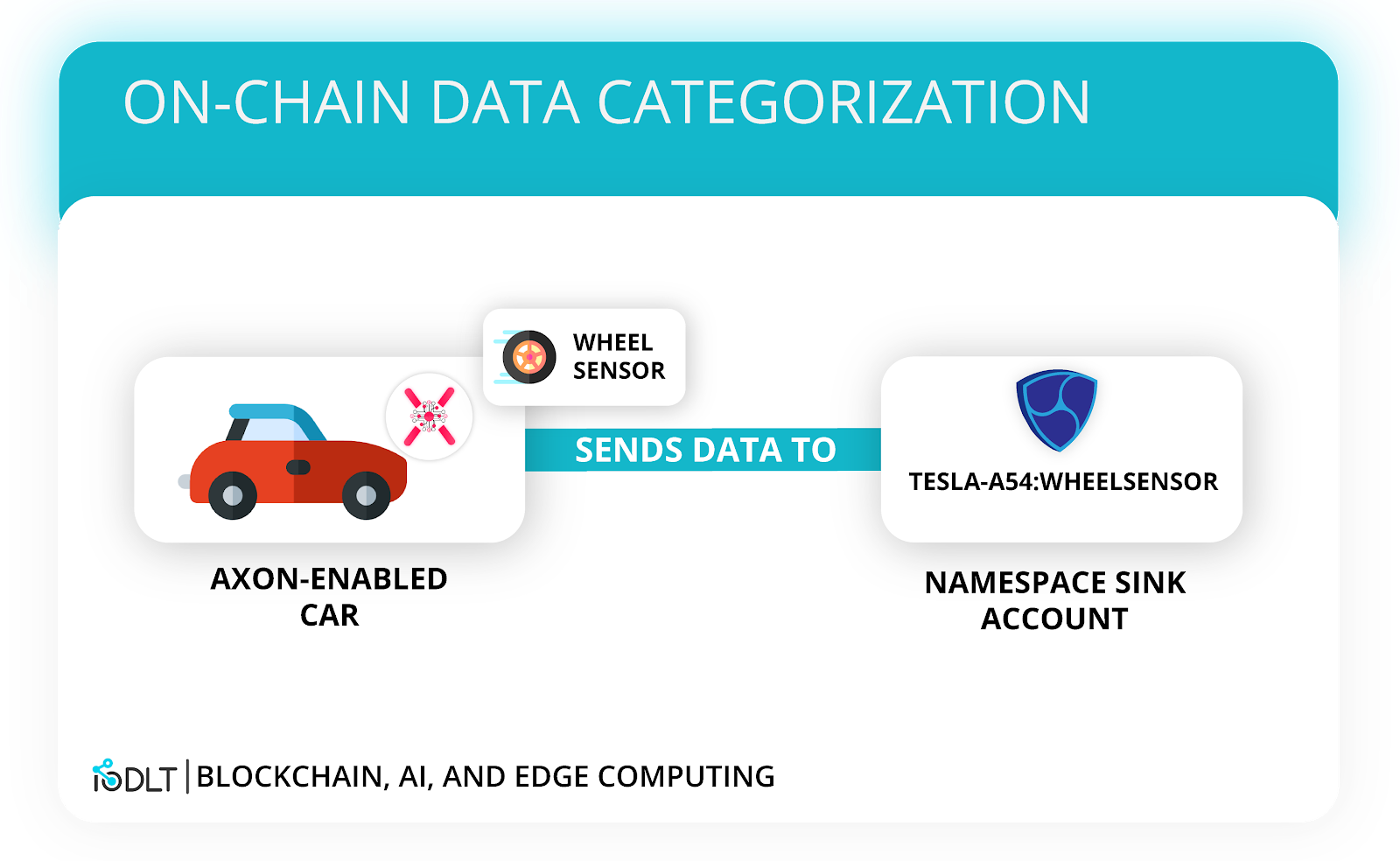
Data Categorization With Catapult Namespaces
Namespaces on Catapult provide an easy and human-readable way to categorize IoT data. By assigning certain accounts with specific tags, devices that record, for example, wheel data from a specific Tesla vehicle know where to record their results.
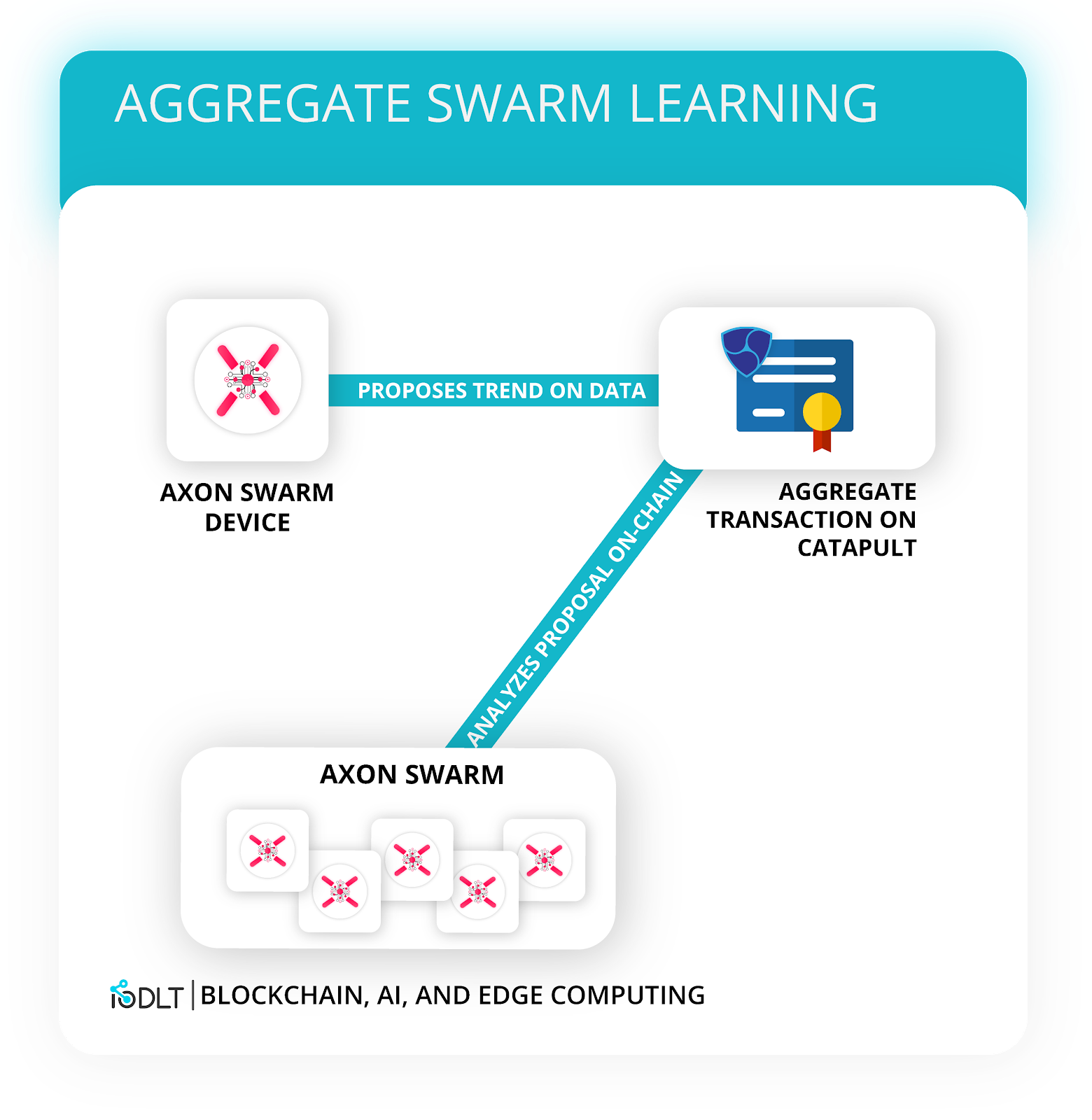
Autonomous Consensus With Aggregate Contracts
Aggregate transactions, which are one-time, atomic smart contracts, can allow an individual Axon to share their multiple conclusions on specific data. Using Aggregate transactions, an Axon device can put a “proposal” on how specific data should look like. Other devices, that make up the swarm, can agree with the conclusions on this data by signing on the transaction. Once the Aggregate transaction is signed with a sufficient number of cosignatories, it gets added to the blockchain as an immutable, permanent record under the correct data category.
Finalize Edge Data With Metadata
Metadata on Catapult can be used to update a data category with the latest information agreed upon from the swarm. To get a glimpse at the latest conclusion from the Axon Swarm, all is needed is a simple API query.
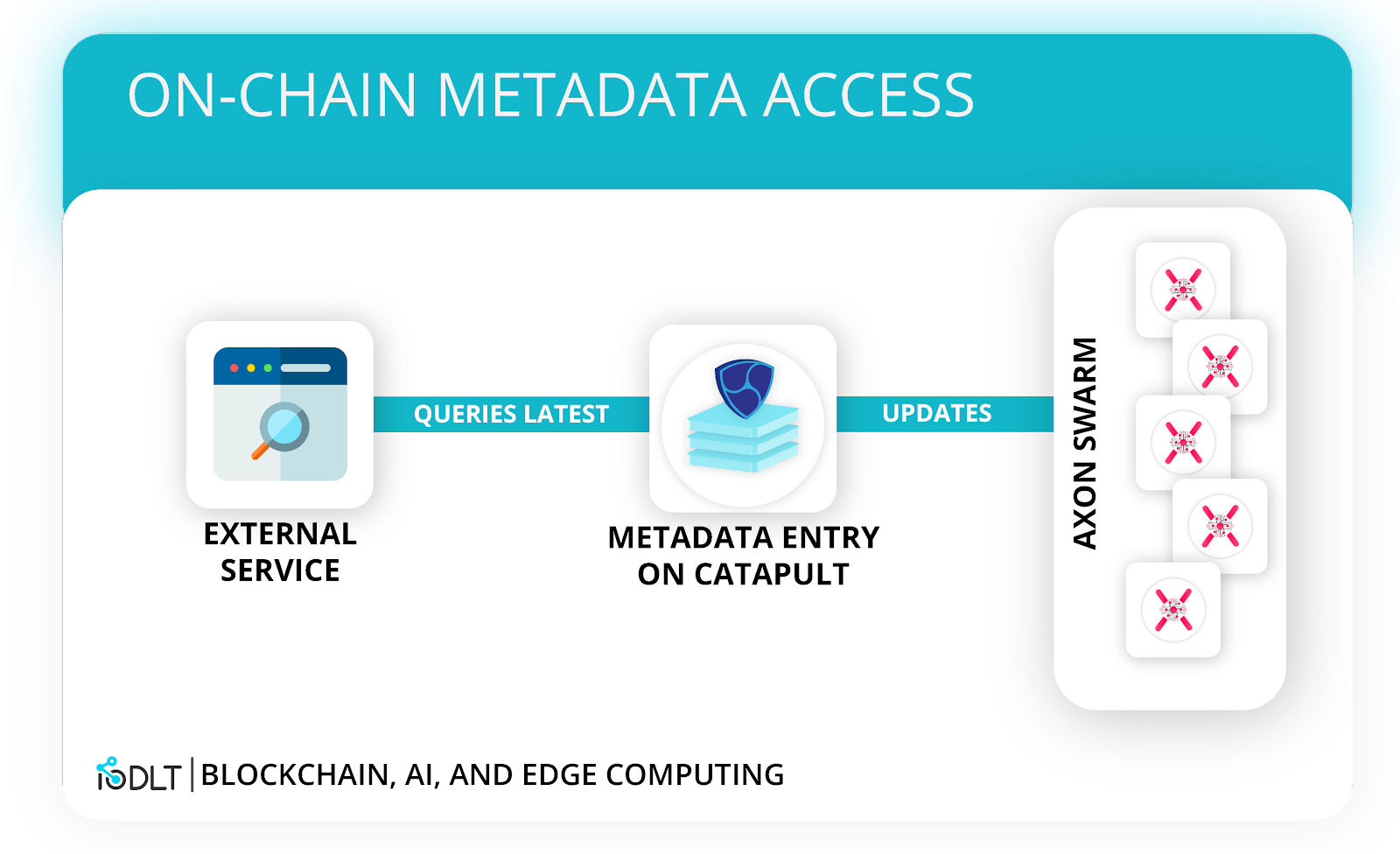
As blockchain is inherently secure, there is a very unlikely chance that this platform would be hacked or compromised in any way. This means that devices can be constantly learning and sharing information 24/7 without any human intervention.
Practical Example: P2P Hospital Communications

To tie the above concepts into one, coherent, and practical example, edge computing, blockchain, and AI / swarm learning can be very useful in a hospital setting. In this example, there will be two hospitals: Hospital A and Hospital B. Sharing of data between the two hospitals can be very valuable. However, the biggest challenge is rendering the shared data to be compliant with HIPAA and GDPR regulations.
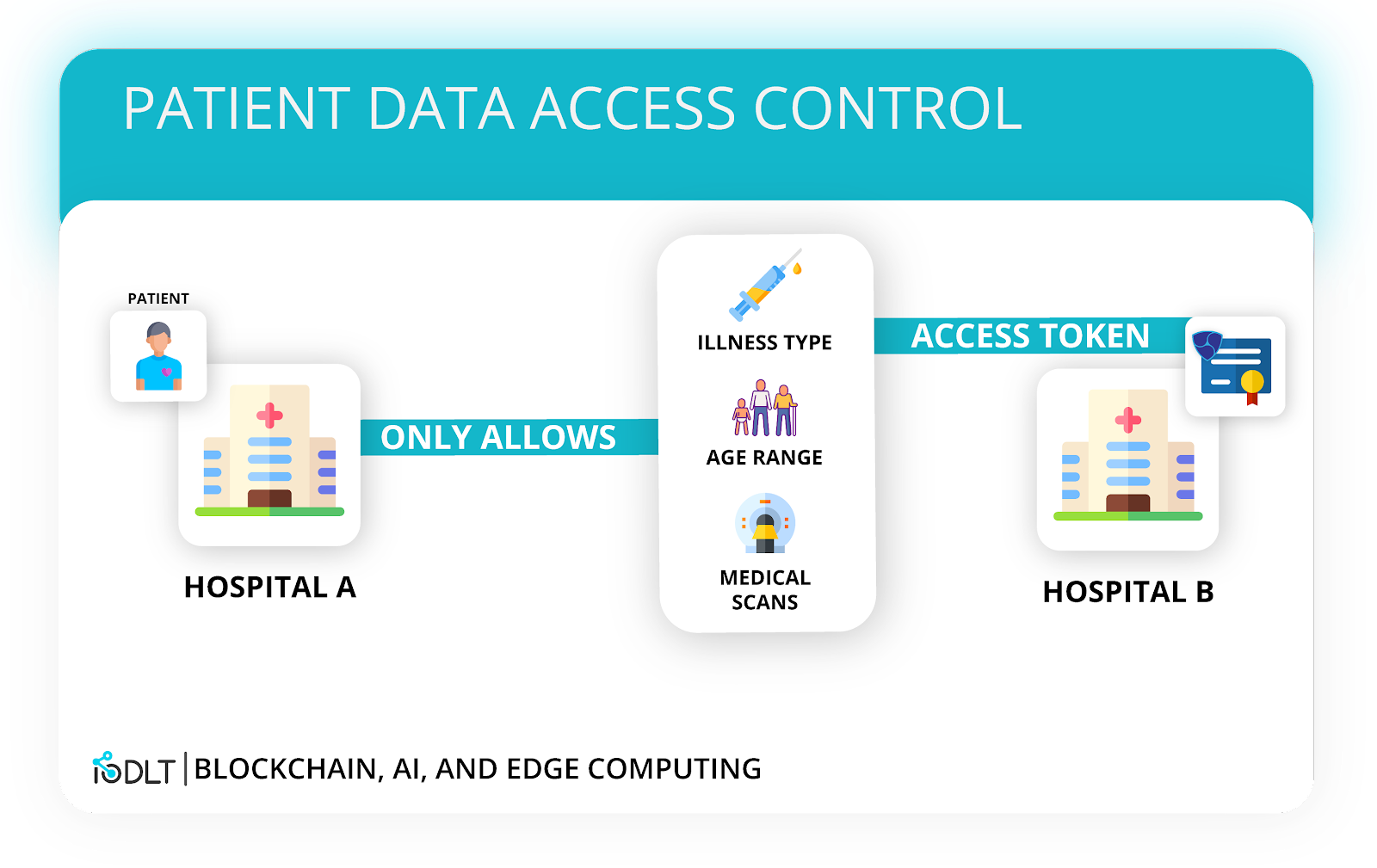
Each hospital is situated in two neighboring cities, and both use a Catapult blockchain as a means of communication. On Catapult, there is the ability to integrate access control for sensitive data. Using a combination of a cryptographic secret sharing mechanism and Catapult’s smart mosaics (tokens), certain individuals within a hospital can be assigned an appropriate level of access to patients’ sensitive information.
For example, a doctor may have permission on-chain to view all aspects of a patient’s health. An administrative worker, however, may only be able to view the patient’s name and healthcare provider.
Using this mechanism, Hospital B can be assigned a level of access for sharing patient data. Only relevant data that has been de-identified as per regulatory standards would be shared to Hospital B, and this would be reflected on-chain.
As Axon supports medical sensors and, and eventually integration with existing medical equipment, Axon is able to be utilized with existing patient monitoring and measurement systems to record information to the blockchain.
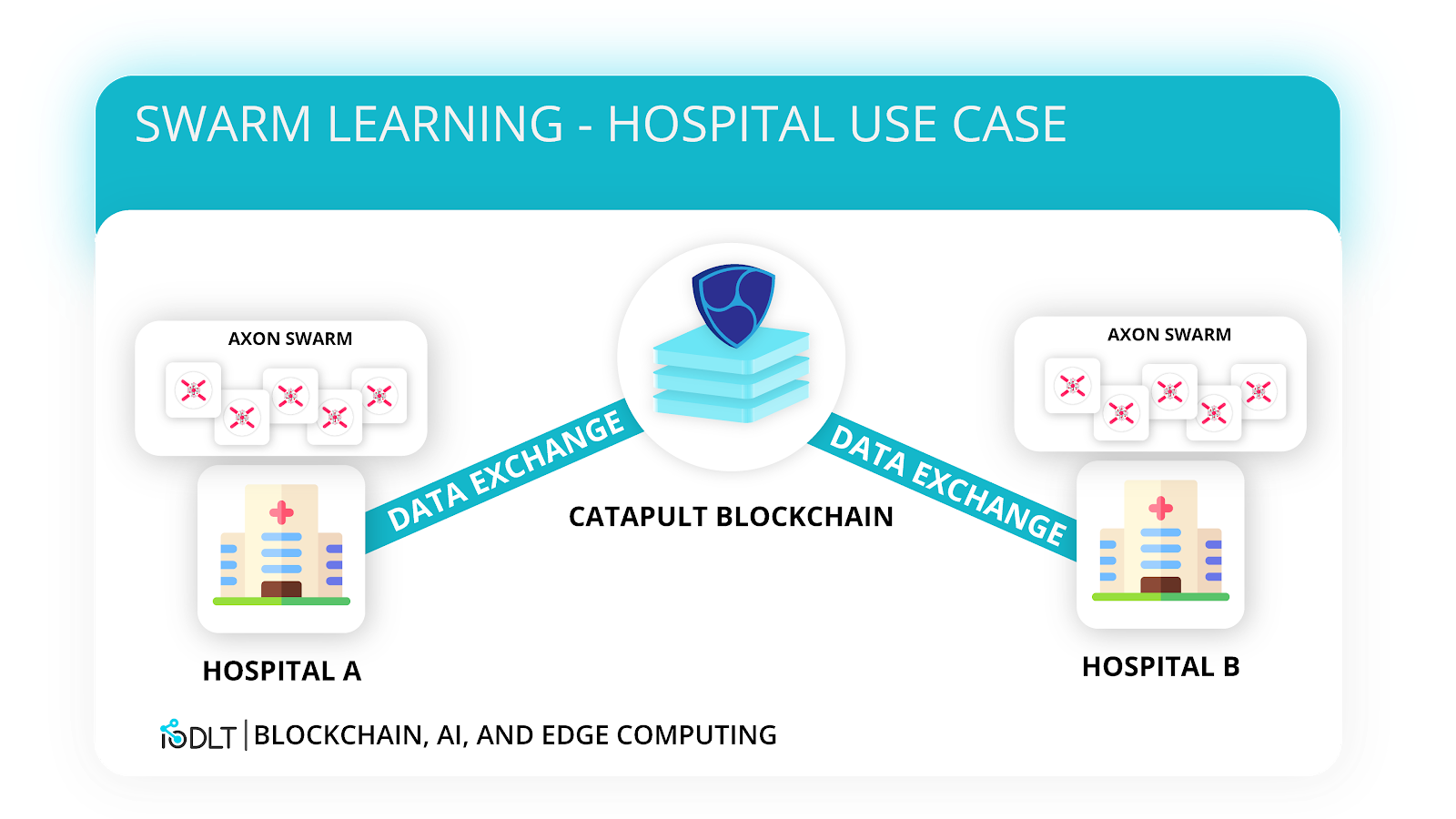
Here is where AI comes into play: if Hospital A receives many cases of tuberculosis, the Axon-enabled medical devices soon learn (through swarm learning) how exactly a scan of tuberculosis infection in the chest looks like.
Likewise, if Hospital B receives excessive cases of pneumonia, the scanning devices in Hospital B can also learn what it looks like for a patient to have pneumonia. As both of these hospitals have thousands of cases to learn from, the predictions for how these illnesses transpire and present can become quite accurate (given that there is a large enough sample). Both hospitals can also log which treatments are used, how effective they are, and what the best treatment is for these specific illnesses.
However, what if Hospital A receives a case of pneumonia that matches that of Hospital B?
Hospital A can query nearby hospitals on the same Catapult network to see if there is a match for this unusual case. As Hospital B already contains extensive information on pneumonia at various stages, patient-types, treatment methods, and symptoms, it can share with Hospital A the conclusions of thousands of cases of pneumonia without Hospital A having to process it at all! Hospital A can now quickly offer a treatment method that has shown to work with Hospital B, furthuring the diagnosis and treatment of the patient at a much faster rate, and allowing the hospital to work at a very efficient pace.
These technologies not only save money - they have the potential to have life changing uses such as furthering medical research, and providing patients with a much better, targeted, and faster treatment.
Conclusion
Edge computing, AI, and blockchain are a powerful and world-changing combination. The ability to calculate meaningful and relevant data on the edge optimizes the current IoT infrastructure, and allows for a scalable future for IoT.
Swarm learning and AI are the concepts that makes this possible, as a network of millions of devices can all learn the relevant data from the edge to form even more accurate and predictable models.
Blockchain is the bridge that allows for swarm learning to occur from the edge, as it acts as a secure, trusted repository for all types of data. In the coming years, we should expect to see implementations take place that utilize all three of these technologies to form a global, scalable, and secure physical-to-digital network.
About IoDLT
Founded in 2018, IoDLT (Internet of Distributed Ledger Technology) utilizes two disruptive technologies – Internet of Things and blockchain – to provide seamless, secure, and scalable B2B solutions. IoDLT brings security to small and large businesses alike, without compromising user data privacy and user-to-business interactions. Their technology’s application spans a wide range of industries, namely healthcare, agriculture, supply chain, and energy metering.
Alongside providing business solutions, IoDLT envisions a future run by embedded devices. Securing those devices will become imperative to the operations of any business. IoDLT deploys proprietary and affordable IoT to blockchain protocols to secure the devices of the world